
The packages kmod-ipt-tproxy and iptables-mod-tproxy are missing from the release repositories and need to be downloaded and installed manually. Unfortunately, at the time of writing, the operating system shipped with the NanoPi (FriendlyWrt fork of OpenWrt) has some issues and doesn't allow an easy installation of shadowsocks. The NanoPi R2S is a cheap little device with two ethernet ports that can easily be plugged between the modem and wifi router to provide tunneling service to your entire network, even if the wifi router doesn's support OpenWrt (or you don't want to change it due to warranty reasons).
SHADOWSOCKS CLIENT UPDATE
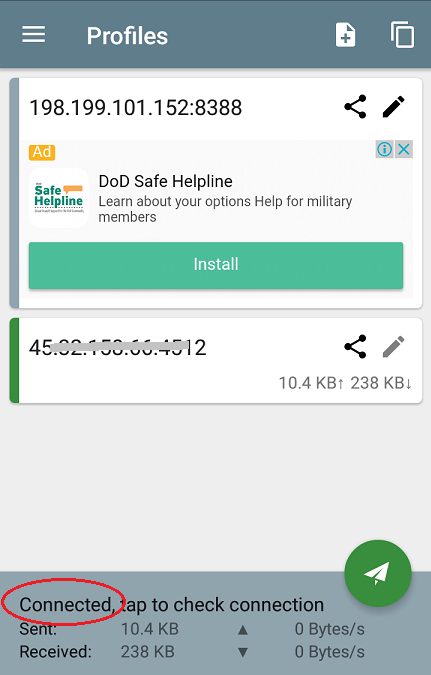
I hope this small guide helps you setting up your shadowsocks tunnel! Feel free to comment and update the content, if necessary.Īdditional steps required for shadowsocks on a NanoPi R2S: This must be done via command line according to the instructions in You can do this either via command line or in the web interface. Follow the steps outlined in the readme file under Recipes > forward all: The simplest recipe is to forward all traffic through the tunnel. Set at least IP, port, method and password, and don't forget to untick the Disable checkbox. In the Luci Web UI, head to Services > Shadowsocks-libev > Remote Servers and edit the existing sss0 server (or add a new one).
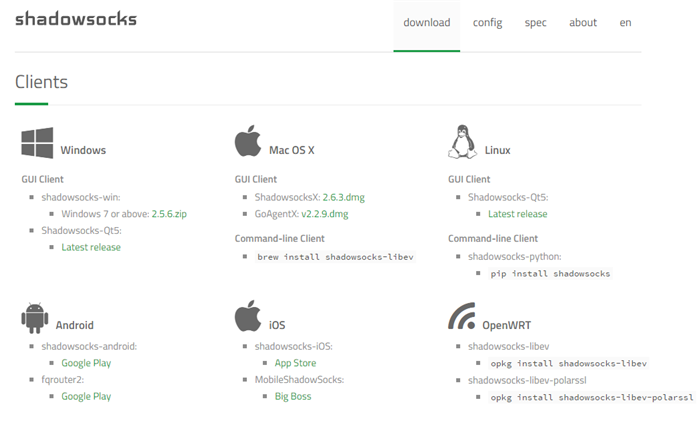
SHADOWSOCKS CLIENT INSTALL
Install the following packages using opkg: These are working at the time of writing. The names of the packages have changed from what many guides state.
SHADOWSOCKS CLIENT HOW TO
Thus, here's a summary on how to install and setup shadowsocks on a fresh OpenWrt installation: Usually commercial software or games are produced for sale or to serve a commercial purpose.As an OpenWrt and proxy beginner, I've spent quite a lot of time figuring out how to set up shadowsocks on OpenWrt due to many outdated guides, how-tos and forum discussions.
Even though, most trial software products are only time-limited some also have feature limitations. After that trial period (usually 15 to 90 days) the user can decide whether to buy the software or not. Trial software allows the user to evaluate the software for a limited amount of time. Demos are usually not time-limited (like Trial software) but the functionality is limited.
In some cases, all the functionality is disabled until the license is purchased. Demoĭemo programs have a limited functionality for free, but charge for an advanced set of features or for the removal of advertisements from the program's interfaces. In some cases, ads may be show to the users. Basically, a product is offered Free to Play (Freemium) and the user can decide if he wants to pay the money (Premium) for additional features, services, virtual or physical goods that expand the functionality of the game. This license is commonly used for video games and it allows users to download and play the game for free. There are many different open source licenses but they all must comply with the Open Source Definition - in brief: the software can be freely used, modified and shared. Programs released under this license can be used at no cost for both personal and commercial purposes.

Open Source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify or enhance. Freeware products can be used free of charge for both personal and professional (commercial use). Freeware programs can be downloaded used free of charge and without any time limitations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
